Origin: a Latin derivative
meaning "Gift of the Earth."
Part 5: Oxygenated Compounds—Aldehydes
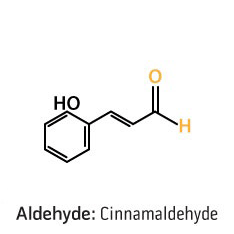
Aldehydes occur at the end of a carbon chain and include an oxygen with a double bond and a hydrogen (usually written C-H-O). This type of constituent can also be distinguished by looking at the scientific name, which usually ends with the suffix "-al" or "aldehyde" as a second word. Although usually found in plants in small quantities, aldehydes are known for their distinctly potent fragrances and are often key contributors to the overall aroma of an essential oil. For example, the aldehyde citronellal is a minor constituent in Melissa essential oil; however, it has been identified as one of the primary contributors to this oil’s sweet lemony fragrance. Aldehydes can cause skin irritation when used topically with sensitive skin types, so appropriate dilution should be used. Common aldehydes found in essential oils are cinnamaldehyde, geranial, and neral.
Main Health Effects:
- Protects against environmental threats1
- Calming to the emotions2
- Helps support healthy gastrointestinal function and digestion3*
| Essential Oil | Main Aldehyde Constituent(s) | Amount |
| Cassia1,2 | cinnamaldehyde, benzaldehyde | Approximately 90% |
| Lemongrass3* | geranial, neral | Approximately 75% |
| Cinnamon1 | cinnamaldehyde | Approximately 70% |
| Cilantro3* | decenal | Approximately 45% |
| Melissa1,2 | geranial | Approximately 35% |





