Origin: a Latin derivative
meaning "Gift of the Earth."
- Shop
-
Our Story
- View Our Story Home
-
Who we are...
-
Who we are...
An essential oil company changing the world one drop at a time.
- About doTERRA
- Our Story
- Executives
- Science
-
-
What we do...
-
What we do...
Provide pure, high quality essential oils and products.
- About Essential Oils
- What is an essential oil?
- Why doTERRA?
- Essential Oil Safety
-
-
Why we do it...
-
Why we do it...
To empower you and your loved ones to live a wellness lifestyle.
- The dōTERRA Difference
- Co-Impact Sourcing
- CPTG® Quality Control
- Global Botanical Network
- Product Innovation
- Source to You
- Co-Impact Sourcing Projects
- Bulgaria
- Guatemala
- Additional Projects
-
-
dōTERRA[doh-ter-ah]
Video disabled by your privacy settings
-
Discover
- View Discover Home
- Healing Hands
- Product Education
- Blog
- Tools
-
doTERRA Events
 See All Events
See All Events
- Resources
- Help
Part 6: Phytochemistry—Alkaloids
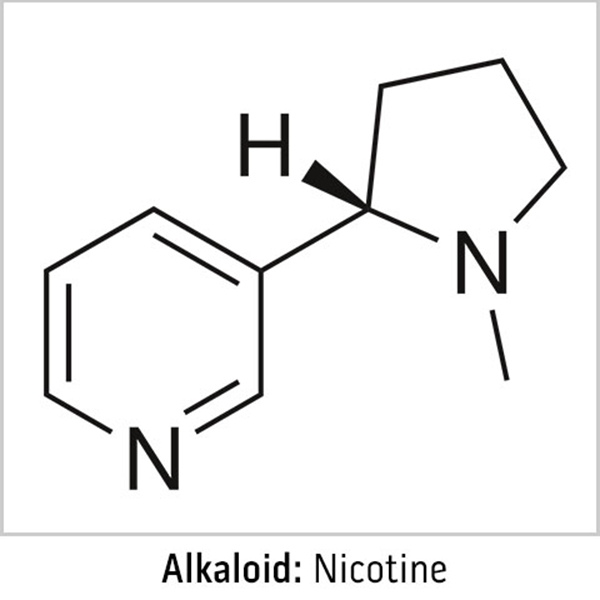
Alkaloids are thought to be the largest class of naturally occurring compounds produced by plants that typically contain one or more nitrogen atom as part of their structure. In general, alkaloids are known as defensive molecules and are extremely effective at warding off dangerous herbivores. Usually these molecules are bitter to the taste (to prevent the herbivore from continuing to eat) or are poisonous. Because the structure of these molecules contains nitrogen components, they are able to work as agonists or antagonists in the neurological systems of animals. This means they can take the place of neurotransmitters in the body and interfere with their normal course of action, causing toxic consequences. Although dangerous to some organisms, many unique and recreational applications for alkaloids have been discovered. Examples of alkaloids are ephedrine, caffeine, cocaine, morphine, and nicotine.
-
Share
- Share on Facebook
- Tweet this
- Pin it
-
Get Link
- Hi-Res Image




